New Signaling Pathway in Neurons
02/25/2021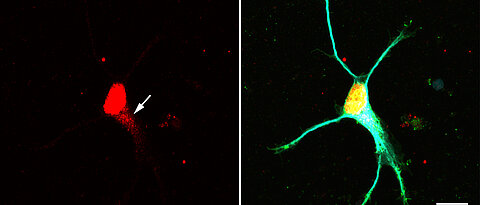
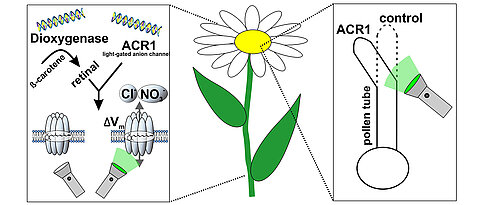
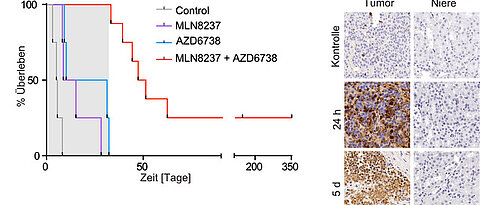
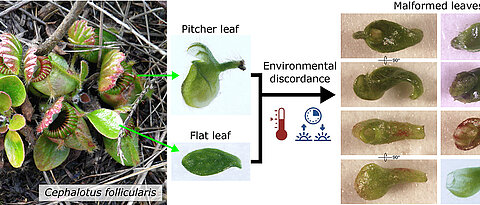
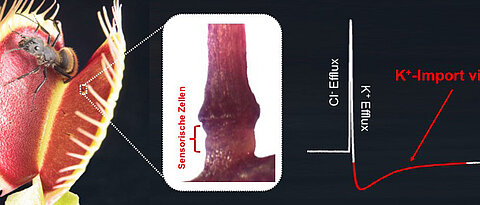
A new signaling pathway has been identified that can prevent the overproduction of certain RNA-protein complexes in neurons. These complexes play an important role in neurodegenerative diseases.
more