A New RNA Catalyst From the Lab
10/28/2020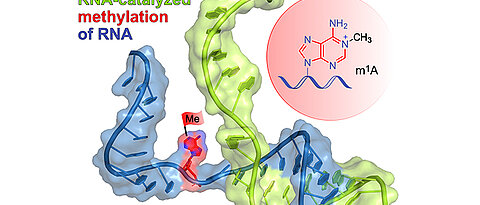
On the track of evolution: a catalytically active RNA molecule that specifically attaches methyl groups to other RNAs – a research group from the University of Würzburg reports on this new discovery in "Nature".
more