Touchable Corona Viruses
08/06/2020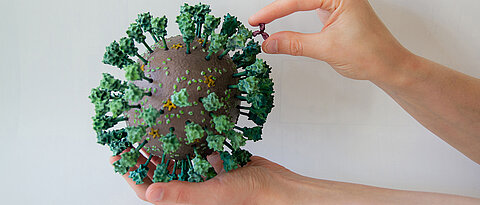
A Würzburg research group prints the first biologically correct 3D model of the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
more
A Würzburg research group prints the first biologically correct 3D model of the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
more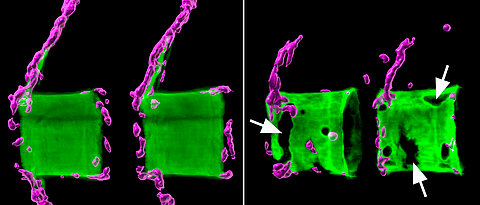
An international research team has found a new approach that may be able to reduce bone loss in osteoporosis and maintain bone health.
more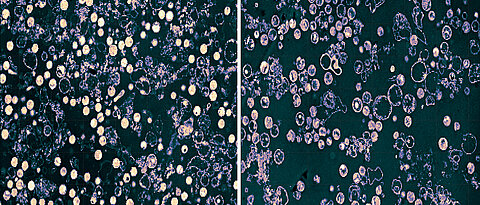
If chlamydiae want to multiply in a human cell, the first thing they need is a lot of glutamine. Würzburg researchers have clarified how the pathogenic bacteria obtain this substance.
more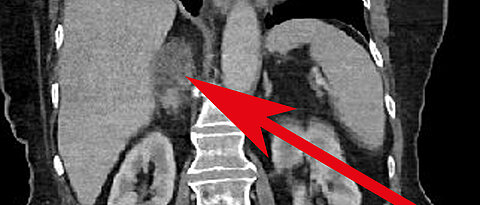
Using a simple urine test alongside routine imaging for patients with adrenal masses could speed up adrenal cancer diagnosis, improving patient’s prognosis and reducing the need for invasive diagnostic procedures, a new multi-centre study has found.
more
The prestigious CWTS Leiden Ranking, which compares the research excellence of universities and their faculties worldwide on the basis of publication and citation figures, gives top marks to the JMU.
more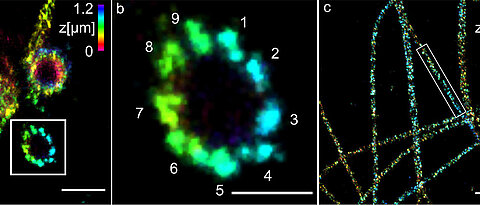
The smallest cell structures can now be imaged even better: The combination of two microscopy methods makes fluorescence imaging with molecular resolution possible for the first time.
more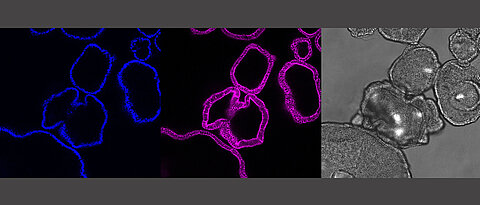
Researchers at Würzburg University are using mini-organs to model the digestive tract in the laboratory. These so-called organoids provide insights into the inflammatory processes that play a role in diseases such Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis.
more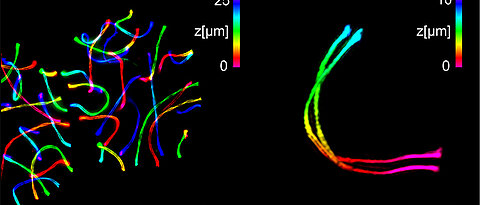
New details are known about an important cell structure: For the first time, two Würzburg research groups have been able to map the synaptonemal complex three-dimensionally with a resolution of 20 to 30 nanometres.
more
Explosive volcanic eruptions are possible deep down in the sea – although the water masses exert enormous pressure there. An international team reports in the journal "Nature Geoscience" how this can happen.
more
No year has been as hot and dry as 2018 since climate records began. Central European forests showed severe signs of drought stress. Mortality of trees triggered in 2018 will continue for several years.
more
Using a newly developed method, Würzburg researchers were able to identify thousands of cryptic peptides on the surface of cells for the first time. These findings could provide a new starting point for cancer immunotherapy.
more
The Quantum Alliance, in which the Cluster of Excellence ct.qmat (Würzburg-Dresden) is represented, welcomes the German government’s initiative to promote quantum technologies. It includes two billion euros for quantum technologies.
more
The Nature Index 2020 is an indicator of the University of Würzburg's strong research performance in natural sciences and life sciences, ranking 104th in the world and 5th in Germany in the recently published ranking.
more
Some galaxies may have two black holes at their centers. This is shown by the analysis of the gamma rays emitted by them. Würzburg astrophysicist Sara Buson was involved in the study.
more
A standard drug for the treatment of depression might also be effective against Covid-19, a new study by Würzburg scientists shows which has been published on a preprint server.
more