Protein Spheres Protect the Genome of Cancer Cells
11/23/2022Hollow spheres made of MYC proteins open new doors in cancer research. Würzburg scientists have discovered them and report about this breakthrough in the journal "Nature".
MYC genes and their proteins play a central role in the emergence and development of almost all cancers. They drive the uncontrolled growth and altered metabolism of tumour cells. And they help tumours hide from the immune system.
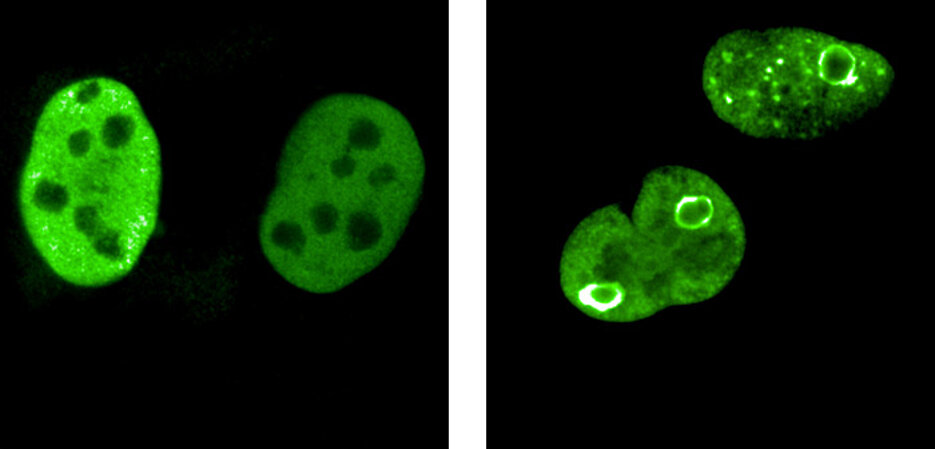
MYC proteins also show an activity that was previously unknown – and which is now opening new doors for cancer research: They form hollow spheres that protect particularly sensitive parts of the genome. If these MYC spheres are destroyed, cancer cells will die.
This was reported by a research team led by Martin Eilers and Elmar Wolf from the Institute of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg (JMU, Bavaria, Germany) in the journal "Nature". The researchers are convinced that their discovery is a game changer for cancer research, an important breakthrough on the way to new therapeutic strategies.
Hollow spheres protect sensitive DNA sites
What the researchers discovered: When cells in the lab are kept under stress conditions similar to those found in fast-growing tumour cells, the MYC proteins in the cell nucleus rearrange themselves in a dramatic way. They join together to form hollow spheres consisting of thousands of MYC proteins.
The hollow spheres surround and protect individual, particularly sensitive sites in the genome – precisely the sites where two types of enzymes can collide: Enzymes that read DNA to synthesize RNA and enzymes that duplicate DNA. Both can be thought of as two trains travelling on only one track, on DNA.
The hollow spheres thus prevent the two enzymes from colliding. The Würzburg team was able to confirm this observation in cancer cells. If the protective function of the protein spheres is switched off experimentally, collisions of the enzymes occur and, as a consequence, multiple breaks occur in the DNA – which ultimately kill the cancer cells.
Search for specifically effective drugs
"These observations revolutionize our understanding of why MYC proteins are so crucial for the growth of tumor cells," says Martin Eilers. The new findings also raise the question of whether drugs can be developed that specifically prevent the formation of the hollow spheres.
To drive this development forward, Eilers and Wolf have started a company. Together with JMU and partners from the pharmaceutical industry, the search for drugs that interfere with the newly discovered functions of the MYC proteins has begun.
"The fact that investors made it possible for us to set up so quickly is certainly not an everyday occurrence," say the JMU professors. They also consider this as a sign that they have made a discovery that is very promising.
Publication
Multimerization of MYC shields stalled replication forks from RNA polymerase. Nature, 23 November 2022, DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-05469-4
Contact
Prof. Dr. Martin Eilers, Biocenter, University of Würzburg, T +49 931 31-84111, Martin.Eilers@biozentrum.uni-wuerzburg.de
Funding
The work was funded by the Deutsche Krebshilfe - German Cancer Aid, the German Research Foundation, and the European Research Council (ERC Advanced Grant AuroMYC, ERC Synergy Grant ULTRARESOLUTION, and ERC Starting Grant TarMYC).