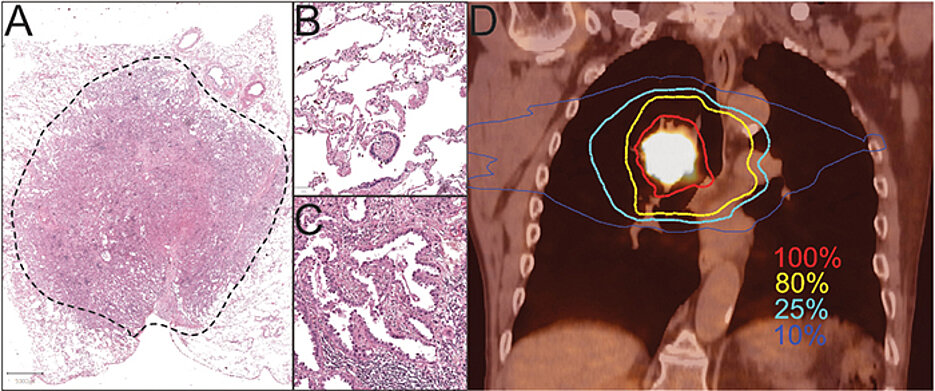
Lung Cancer: When Radiotherapy Fails
07/01/2022Some lung tumours do not respond to radiation therapy. This effect can be reversed by blocking an enzyme in the tumour cells, as Würzburg researchers report.
Lung cancer is the most common cancer in the world, with 2.2 million new cases and around 1.8 million deaths in 2020 alone. Although knowledge about the disease has improved considerably, and new therapeutic strategies can prolong the lives of previously incurable patients, the numbers clearly show that lung cancer is still a serious disease and the mortality rate is still far too high.
To further reduce the number of deaths from this type of tumour, novel and improved treatments are needed. Würzburg researchers are concentrating on radiotherapy. In combination with chemotherapy, this is still one of the most important treatment approaches. This is especially true for late-stage non-small cell lung tumours, where treatment options are rather limited.
PTEN mutation is suitable as a biomarker
In this type of lung tumours, radiotherapy can be ineffective. This is due to the interaction of a common, specific mutation in the PTEN gene with the DNA repair enzyme ATM, as the Würzburg team found out.
However, lung tumours, in which this mutation occurs, can be therapeutically influenced. With two experimental inhibitors, the researchers succeeded in blocking the DNA repair enzyme in the tumour cells. As a result, the tumours became sensitive to radiation again and could be killed in tumour models.
Inhibitors in preclinical testing
"Such inhibitors have not yet been approved for use in humans, but partake in clinical trials," explains cancer researcher Dr. Markus Diefenbacher from the Biocentre at the University of Würzburg. His team has published the new findings in the journal Cell and Bioscience together with a group led by radiotherapist Dr Thomas Fischer from Professor Michael Flentje's research group at the University Hospital Würzburg.
If the inhibitors pass the clinical tests, they offer a new opportunity: the PTEN mutation is suitable as a biomarker that indicates a tumour's resistance to radiation. With corresponding analyses, one could specifically identify patients who might benefit from a combination of inhibitor and radiotherapy. This could be realised quickly: patients with non-small cell lung cancer are already routinely examined for PTEN and other disease-relevant mutations.
Focus on radiation dose reduction
Currently, several clinical trials are looking at the impact of PTEN and ATM on treatment outcomes. "We are confident that our new findings will generate a lot of interest in pursuing this innovative strategy for the treatment of non-small cell lung tumours," says Professor Michael Flentje.
Radiotherapy is a mainstay in the treatment of late-stage tumours of the respiratory tract and other organs. The Würzburg team is therefore continuing to research new strategies and targets. One focus is on reducing the radiation dose in such a way that the desired therapeutic success is still achieved and at the same time the healthy tissue around the tumour is spared as much as possible.
Publication
Fischer, T., Hartmann, O., Reissland, M. et al. PTEN mutant non-small cell lung cancer require ATM to suppress pro-apoptotic signalling and evade radiotherapy. Cell Biosci 12, 50 (27 April 2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-022-00778-7
Sponsors of the work
This research work was financially supported by the Deutsche Krebshilfe, the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, the German-Israeli Foundation and the Interdisciplinary Centre for Clinical Research Würzburg.
Cooperation partners
The results were obtained by clinical researchers, biochemists, biologists, radiotherapists and surgeons. Led by the translational research group of Dr. Markus E. Diefenbacher and the radio-oncology group of Professor Michael Flentje, collaborators from the Würzburg pathology department (Dr. Gerhard-Hartmann and Dr. Mathias Rosenfeldt), the Robert Bosch Hospital Stuttgart (Professor Hans-Georg Kopp), the Dr. Margarete Fischer-Bosch Institute for Clinical Pharmacology Stuttgart (PD Dr. Frank Essmann) and the Institute for Biochemistry II of the Goethe University Frankfurt (Dr. Christian Münch) provided significant support for the work.