MA 120: Single Major
Fachspezifische Bestimmungen (in German)
- Module Catalogue (Modulhandbuch)- Version 2025, amtliche Veröff.: 2025-39 (07.05.2025), von 2025-WiSe, Uniquename: 88|n02|-|-|H|2025
deutsch: MHB1-de-88-n02-H-2025, MHB2-de-88-n02-H-2025, SFB-de-88-n02-H-2025
english: MHB1-en-88-n02-H-2025, MHB2-en-88-n02-H-2025, SFB-en-88-n02-H-2025
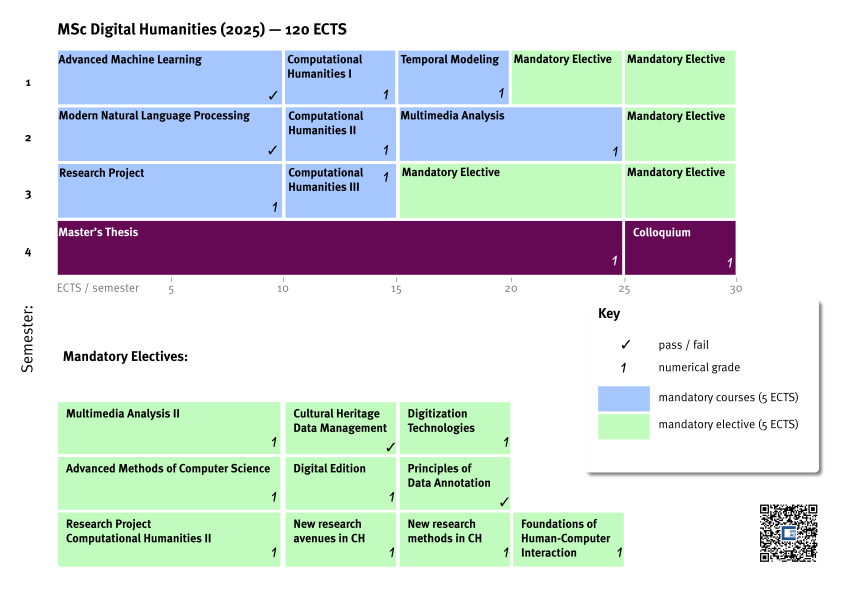
First Semester
- Lecture: Deep Learning (Katharina Breininger), see WueStudy
- Exercise (Katharina Breininger), see WueStudy
- Tutorium (Christof Weiß)
The lecture provides advanced knowledge of deep learning techniques such as FCN, CNN and LSTMs, practical application examples for NN architectures, e.g. in the field of image and speech processing. Current models and methods of machine learning and their technical background are presented. Building on this, models from the field of deep learning, such as CNNs, RNNs and sequence-to-sequence architectures, are discussed. The theoretical foundations of these models, such as training through backpropagation, are also discussed in detail. For all the models covered, it is shown how they are used in practice for specific problems such as image processing and text generation.
Goals
Students have knowledge of the possible applications and limitations of deep learning, of important architectures and how they are implemented in typical tools, of the ability to reprogram network structures from the literature, of data preparation and of solving concrete tasks.
The course teaches the skills needed for the systematic analysis of written cultural data, e.g., literary texts or texts from social media. This includes the following tasks: Formulating a research hypothesis based on existing research and developing a research design to test it, automated extraction of specific text features including evaluation of the extraction method, and statistical analysis of the data.
Goals
Students are able to independently implement at least one typical research design in CH, make informed decisions about the extraction and analysis methods to be used, and implement them technically.
Central questions in the humanities and cultural studies focus on the analysis of dynamic processes and historical developments rather than static snapshots. The computer-assisted investigation of such diachronic phenomena requires specific methods of data preparation and quantitative analysis. This module introduces the theoretical foundations and practical application of temporal modeling, in particular statistical time series analysis and related machine learning methods.
Goals
Students learn how to prepare diachronic data and analyze historical developments using quantitative methods. The focus is on the practical application of methods such as time series and trend analysis in order to test periodization hypotheses or uncover patterns in historical data.
additionally, choose 10 ECTS from the mandatory electives.
Second Semester
- Languages of the world: language families, typology, etymology.
- Linguistic universals: words, morphology, partsof-speech, syntax. Alphabets (scripts), encoding, and language identification.
- Multilingual word representation spaces (aka cross-lingual word embeddings).
- Transformer architecture and Pretrained (multilingual) Language Models.
- Machine translation.
- Multilingual resources: unlabeled corpora, lexico-semantic networks and word translations, parallel corpora.
- Cross-lingual transfer: from word alignment and label projection, over MT-based transfer to zero-shot and few-shot transfer with multilingual Transformer-based language models.
- Advanced topics: curse of multilinguality, modularization and language adaptation, multilingual sentence encoders, contextual parameter generation, multi-source transfer, gradient manipulations.
Goals
Students will acquire theoretical and practical knowledge on modern multilingual natural language processing and also get an insight into cutting edge research in (multilingual) NLP. They will learn how to represent texts from different languages in shared representation spaces that enable semantic comparison and cross-lingual transfer for various NLP tasks. Upon successful completion of the course, the students will be well-equipped to solve practical NLP problems regardless of the language of the text data, and to determine the optimal strategy to obtain best performance for any concrete target language.
Format
Lecture with Exercise and Tutorium.
Courses in WueStudy include:
Multilingual Natural Language Processing (Goran Glavaš)
Machine Learning for Natural Language Processing (Andreas Hotho)
Processing and discussion of exemplary research questions using computational humanities methods, with a focus on corpus analysis of non-textual data such as audio, music, image, video, or 3D data.
Goals
Students are able to answer research questions in computational humanities and to carry out and evaluate corpus analyses of non-textual data.
Advanced techniques for the analysis of multimodal data (e.g. audio/music processing, image processing) using machine learning methods. Discussion and evaluation of such methods in the context of the computational humanities.
Goals
Students have a fundamental understanding of the respective data types as well as theoretical and practical knowledge in the field of multimedia processing. They have gained experience with typical tasks and are able to understand, apply, further develop and evaluate the algorithms.
Lectures
Music Information Retrieval (Christof Weiß) (Exercise)
There will be additional offers in the future, e.g., from the area of Computer Vision.
If you are studying the single major (120 ECTS) and visit two of the alternatives, the second course can be accounted for as mandatory elective.
additionally, choose 5 ECTS from the electives.
Third Semester
The research project gives students the opportunity to independently apply what they have learned so far to a topic of their own choosing. Ideally, they should work on a research question from the formulation of the research hypothesis to data collection and analysis, or at least complete a significant step in the process.
Goals
Students are able to work on a problem in the CH, develop procedures for solving it, implement these in appropriate steps, and present the results.
The course teaches the necessary skills for the systematic analysis of cultural data, e.g., literary texts, music, images. This includes the following tasks: Formulating a research hypothesis in consultation with the state of the art and developing a research design to test it, automated extraction of specific features including evaluation of the extraction process, and statistical analysis of the data.
Goals
Students are able to independently implement at least one typical research design in CH, make informed decisions about the extraction and analysis methods to be used, and implement them technically.
additionally, choose 15 ECTS from the electives.
Fourth Semester
In the 4th semester, you should write your master’s thesis and finally present it in the colloquium.
Mandatory Electives
There are varying offerings that can be used as mandatory elective courses. You will need a total of 30 ECTS. Please check WueStudy for the individual offerings in each semester, not every module will be offered in every semester.
Advanced techniques for the analysis of multimodal data (e.g. audio/music processing, image processing) using machine learning methods. Discussion and evaluation of such methods in the context of the computational humanities.
Goals
Students have a fundamental understanding of the respective data types as well as theoretical and practical knowledge in the field of multimedia processing. They have gained experience with typical tasks and are able to understand, apply, further develop and evaluate the algorithms.
Lectures
Music Information Retrieval (Christof Weiß) (Exercise)
There will be additional offers in the future, e.g., from the area of Computer Vision.
If you are studying the single major (120 ECTS) and visit two of the alternatives, the second course can be accounted for as mandatory elective.
The research project gives students the opportunity to independently apply what they have learned so far to a topic of their own choosing. Ideally, they should work on a research question from the formulation of the research hypothesis to data collection and analysis, or at least complete a significant step in the process.
Goals
Students are able to work on a problem in the CH, develop procedures for solving it, implement these in appropriate steps, and present the results.
TODO
Cultural data and research data from the cultural sciences and humanities often pose special challenges in terms of indexing, management and preservation. The data should often be usable for a long period of time and be available for very different applications, if possible also for scenarios that were not considered when the data was created. The seminar teaches relevant principles and techniques.
Objectives
Students understand the challenges of cultural data management, can model cultural data and design and implement techniques for its management.
S (2) • 5 ECTS • NUM • Faculty of Arts, Historical, Philological, Cultural and Geographical Studies
Digital editions make historical documents accessible and prepare them for the questions of a scientific audience. The module teaches the principles and techniques of designing, editing and presenting digital editions.
Objectives
Students understand the functions and characteristics of digital editions and can independently take on roles in the conception, presentation or preparation of digital editions.
S (2) • 5 ECTS • NUM • Faculty of Arts, Historical, Philological, Cultural and Geographical Studies
Data annotation, i.e., the linking of concepts from the humanities and cultural studies with cultural data, is an essential tool for the development and evaluation of automatic processes in the CH. The seminar teaches the relevant work process from the development of annotation guidelines to their technical implementation in an annotation environment, the training of annotators, and the calculation of measures of inter-annotator agreement.
Goals
Students can independently develop an annotation and implement it themselves or supervise its implementation.
Due to their close links to computer science and AI, CH are developing particularly rapidly, which makes it especially important to keep knowledge up to date. Current research trends are discussed using a selected example, e.g., the development of a new form of information representation, information extraction, or data analysis.
Goals
Insight into current research on a selected topic of CH. Acquisition of the competence to compile and understand current research on a selected topic.
New research methods for the computational humanities.
Goals
Students have specialized knowledge of new research methods in computational humanities. They can understand, apply and evaluate these methods.